Related Resources
Do you know what kind of engine powers your cells with energy and enables you to breathe, move, think, and do anything you want?
You may be quick to say that your brain, the ruler of your body, is in charge of all that you do. And although you wouldn’t necessarily be wrong, your brain can’t run on its own. It needs the energy to do its job, right?
So, how does it get it?
Thanks to cellular metabolism!
We explore the importance of metabolism, the way it works, what controls it and how metabolic disorders occur.

What Is Cellular Metabolism?
Cellular metabolism is a series of chemical reactions that transform everything you eat and drink into fuel that gives your body the energy it needs for all key processes, from running to breathing.
This means that metabolic processes convert your meals into energy, also known as calories. (You’ve probably heard that one before!)
Now, cellular metabolism IS your metabolism.
It is often believed that metabolism only has to do with digestion, whereas, in fact, cellular metabolism POWERS your digestion, among other processes in your body!
Your metabolism is working even when you’re asleep or resting.
No matter what you do, cellular metabolism ensures your body has enough energy to perform essential functions, including:
- Breathing
- Thinking
- Growing cells
- Repairing cells
- Digesting food
- Regulating body temperature
The leftover energy — the one that doesn’t go into fueling these autonomous processes — is what empowers your voluntary movements such as walking, dancing, and other physical activity.
When the food you eat is rich with nutrients, you provide your cells with the substances they need to produce energy. This also means that if you avoid nutritious food, you deprive your body of the fuel it needs to run smoothly.
This is why health experts insist on maintaining a varied diet because your body needs proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals to stay healthy and strong!
Speaking of keeping you healthy, the Biowars comic book depicts the battle that rages within every one of us: the mighty Biowarriors, the protectors of the immune system, fighting evil intruders known as microbes.
Your immune system and metabolism are interlinked because the more energy your body has, the stronger your immunity is!

How Does Metabolism Work?
To best describe how your metabolism works, let’s start from the very first step.
Let’s say you’re eating pizza. Mmmm, pizza.
After you swallow the first bite, your digestive system starts to work.
To do its job and process the food, it needs enzymes.
Enzymes are substances in your cells that affect chemical reactions in your body. The majority of them are proteins, but some are RNA molecules.
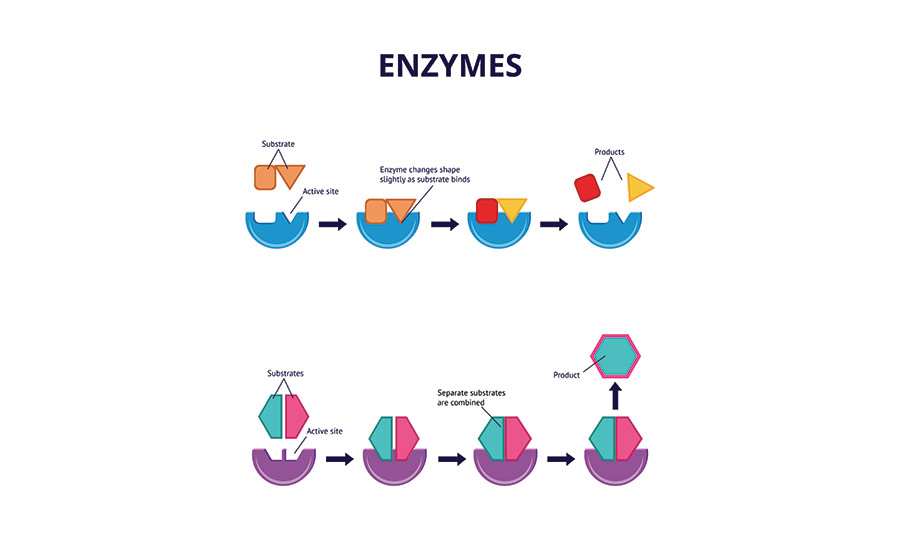
Your cells contain 5,000 types of enzymes that facilitate different chemical reactions. For example, some of the processes that enzymes facilitate include:
- Digestion
- DNA replication
- Hormone production
- Respiration (a fancy term for “breathing”)
When it comes to digestion, enzymes help your metabolism break food into substances that your cells use. For instance, enzymes break the proteins you eat into amino acids (the building blocks of proteins), turn carbohydrates into glucose, and transform fats into fatty acids.
To put it simply: your enzymes break down your food into substances that feed your cells.
Then cells do their work to turn their food into your energy.
It’s a fascinating system you have going there!
Now, your body doesn’t go through just one type of metabolic reactions. In fact, there are two types of cellular metabolism you should know about!
2 Types Of Metabolism
Cellular metabolism can be categorized into two types:
- Catabolism
- Anabolism
The process of catabolism occurs when you digest food.
Catabolic reactions break down the food and drinks you take into simple structures so that cells can use them for metabolic processes. For example, when you eat a piece of cake, catabolic reactions break it into something your body can use for energy, e.g. glucose. Or if you get a slice of pizza, catabolism breaks carbs and fats into energy.
When a person isn’t eating enough or eating well, catabolic processes need to look for energy resources elsewhere. They turn to a person’s own resources and start to break down their stored fat and their muscles into energy.
Anabolism is the opposite of catabolism.
During anabolism, your cells use the energy released during catabolic processes to create complex molecules, such as fat and protein.
Anabolism helps your cells grow and it allows them to store energy.
For instance, your growth is possible thanks to anabolism!
Catabolism and anabolism are examples of metabolic pathways.
What Are Metabolic Pathways?
Metabolic pathways are a series of intertwined chemical reactions that occur on a cellular level.
Every sequence of reactions leads to the conversion of a particular substance into a final product. Substances found at the start of a metabolic pathway are called feeders, while the end result (i.e. the molecules that leave the metabolic cycle, e.g. glucose) is simply referred to as a product.
For instance, photosynthesis is an anabolic pathway. During photosynthesis, plants make glucose. They do so by using sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into glucose, which is the end product of the anabolic pathway in this case.
As for a catabolic pathway, let’s go back to that hypothetical piece of cake we gave you earlier.
When your body breaks down the molecule of glucose, the molecule releases energy. This happens during the process called cellular respiration.
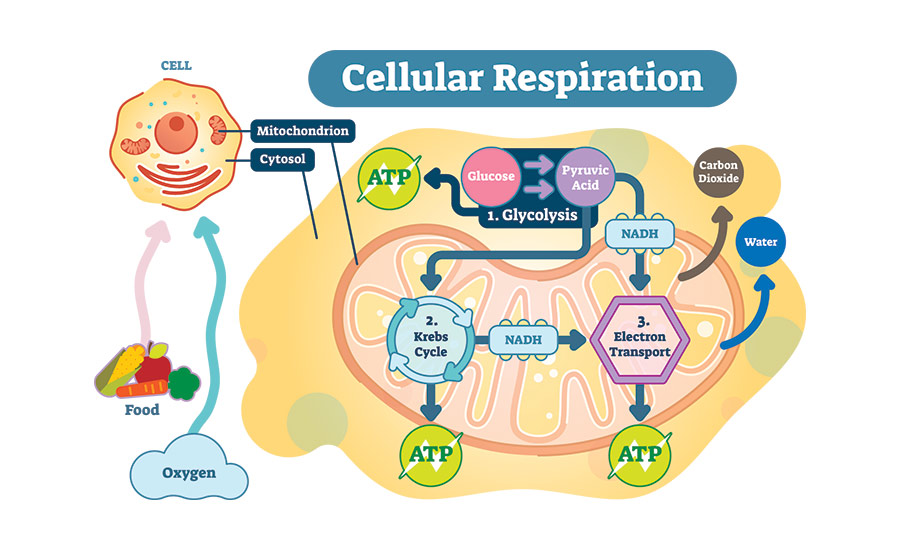
Your cells then capture that energy for a short while. That form of energy is called ATP, which is short for adenosine triphosphate.
Don’t sweat it if you can’t memorize what ATP stands for. What matters is that you understand that your cells need the energy released during cellular respiration.
Your cells then use ATP for other cellular processes, including transporting lipids and proteins in and out of cells, DNA and RNA synthesis and muscle contraction.
The chemical reactions in metabolic pathways can’t happen on their own. Something needs to provoke them, and that something are enzymes!
What Controls Metabolism?
Your metabolism is affected by several factors, including:
- Hormones
- Calories
- Age
- Body size
- Gender
- Genetics
- Physical activity
1. Hormones
Of all the main factors we listed above, hormones can impact your cellular metabolism the most.
Both your thyroid gland, the butterfly-like gland placed at the front of your neck above the collar bone, and the pancreas, a gland behind your stomach, produce hormones that affect the way your metabolism works.
For instance, your thyroid gland makes a hormone called thyroxine (T4), which impacts the speed of metabolic processes in your body.
Aside from T4, the thyroid gland also secretes triiodothyronine (T3).
Together, the two hormones affect many key processes in your body, including your heart rate, brain development and body temperature.
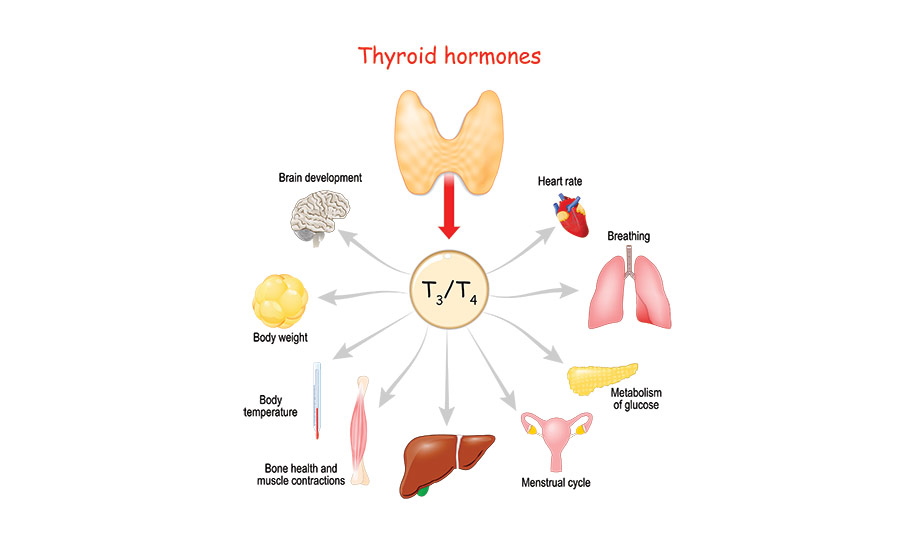
On the other hand, the hormones your pancreas secretes help your body understand if it needs to perform the anabolic or catabolic metabolic activity.
For example, after you eat, the glucose level in your blood increases. The pancreas understands it needs glucose for fuel, so it releases insulin, a hormone that tells the cells they should perform an anabolic process.
2. Calories
Aside from your hormones, calories are another huge factor that affects metabolism.
The more calories you eat, the more leftover energy there is. So, unless you use the extra energy for physical activity, you risk storing calories in your body as fat.
To avoid having weight issues, it’s important you make smart food choices and exercise on the regular.
3. Age
When you’re young and still growing, your metabolism rates are high because your body needs a lot of energy for your growth and millions of other chemical reactions happening on a cellular level in your body.
However, as you age, you lose muscle mass and your hormones change, causing the rate of your metabolism to slow down.
Muscles need more energy than fat, so the bigger the muscle mass, the more energy your body needs to live. This doesn’t mean you should go to the gym and go berserks with weights, but an occasional strength or resistance training may do you good the older you get.
4. Body Composition
If someone has a bigger body, their organs are also larger, so they have a larger basal metabolic rate (BMR).
This means their muscles and other organs need more energy while at rest than someone of smaller build.
5. Gender
As for gender, studies have shown that men have 3-10% faster metabolism than women. That’s because they have more muscle mass and their biochemistry is different.
For example, after a strenuous exercise, a hormone called ghrelin spikes in women. This hormone is the hunger hormone, and when it spikes, it drives people to eat. Men usually don’t have a problem with this hormone fluctuating after a workout, so they probably won’t eat too much when they’re done exercising.
6. Genetics
Genetics also impacts your metabolism.
Some people are born with larger BMR, while others may inherit gene variants that raise the risk of obesity because they’ve been impacted by a particular lifestyle and environmental conditions.
A sedentary lifestyle and increased intake of processed foods of ancestors cause genes to adapt to those conditions, and such genetic material is then passed on to future generations.
7. Physical Activity
In terms of cellular metabolism, exercising is important because it increases your muscle mass. That means your body needs more fuel, so it burns more fat.
Aside from boosting metabolism, physical activity also positively impacts heart rate and blood pressure and is of utmost importance for your heart health.
What Are Metabolic Disorders?
In some cases, the process of cellular metabolism doesn’t run as smoothly as it should. That’s when metabolic disorders occur.
Metabolic disorders affect the way catabolism and anabolism work, causing a person to have either too much or too little of the substances that keep them alive and healthy.
In most cases, people inherit metabolic disorders, but they can also occur when the liver or pancreas don’t work well. Metabolic disorders can also happen when mitochondria, cells’ energy generators, become dysfunctional because of DNA mutations or environmental triggers.
One of the most common metabolic disorders is diabetes. In the U.S. alone, more than 37 million Americans had diabetes in 2019.
Diabetes is a disease that prevents the body from regulating glucose levels in the blood with insulin. When that happens, glucose can’t enter a person’s cell to give them energy. Instead, that person has too much glucose in their blood, which can cause a range of health issues if the condition is not monitored and treated.
Aside from diabetes, some other types of metabolic disorders include:
- Gaucher’s disease: This kind of metabolic disorder affects a person’s ability to break down fat. When that happens, the liver, spleen and bone marrow store excess fat. That can cause a person to suffer from bone damage, but they can also feel tired and bruise easily.
- Hereditary hemochromatosis: This condition messes up a person’s ability to absorb iron. It can cause joint pains and tiredness, but also more serious issues, including stomach issues and heart disease.
- Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD): This is a rare, but life-threatening metabolic disorder. MSUD prevents a person to process certain amino acids, which causes their neurons to degenerate.
- Tay-Sachs disease: This is another rare, inherited metabolic disease. Tay-Sachs disorder is characterized by the absence of an enzyme that breaks down a fatty substance called GM2 ganglioside. In that case, the amount of GM2 grows to toxic levels, especially in neurons, causing neurons to die.
Recap On Cellular Metabolism
Cellular metabolism keeps you alive and kicking.
A series of chemical reactions in your body empowers you with the energy you need to grow, heal, reproduce, run, play football, work and do pretty much anything you want.
Although you can’t control all factors that impact the way your metabolism works, e.g. genetics, you certainly can make sure to treat your body well.
You should try to eat nutritious food so that your cells get just the substances they need to keep you healthy and strong. Regular physical activity is also important for your metabolism because it burns excess fat, and that improves your overall health.